Earthquake Resistance of Buildings in Japan - Structure types (seismic isolation and damping)

To make all structures as earthquake-resistant as possible, the Building Standard Act has been - and always will be - strictly reviewed to ensure that buildings can withstand earthquakes every time the country experiences a large earthquake.
Earthquake-resistance strength is strictly demanded for all buildings, and you cannot obtain building permission unless you can meet a strict requirement of the earthquake-resistance standards stipulated by law. For that reason, compared to other countries, the collapse ratio of buildings due to a powerful earthquake is said to be extremely low in Japan.
We, here, would like to touch on the history of the review of building laws and regulations in Japan, and explain in detail about the earthquake resistance of buildings and how to confirm it for choosing a building that is strong against earthquake. We also would like to explain about types of building structures in Japan, the characteristics, and quake-resistance performance of each type.
The important years when the laws and regulations were revised, for judging the earthquake resistance of buildings in Japan
1971 |
Tightening the standards for RC structures |
|---|---|
1981 |
Enforcement of New Anti-seismic Design Standard |
2000 |
Tightening the standards for wooden structures Commencement of grading anti-seismic performance level under Housing Quality Assurance Act |
Changes in laws and regulations in Japan concerning anti-seismic performance
1971 |
After the earthquake off the shore of Tokachi in 1968(maximum JMA seismic intensity scale 5), the standard for tie-hoops of RC, or reinforced concrete structure, was tightened. |
|---|---|
1981 |
Following the disaster caused by the earthquake off the shore of Miyagi Prefecture in 1978(maximum JMA seismic intensity scale 5), the Building Standard Act was revised and the New Anti-seismic Design Code came into effect. The new standard focuses not only on preventing the collapse of buildings during earthquakes but also on how to secure the safety of the people inside them. |
2000 |
Based on the lessons learned from the Great Hanshin Earthquake of 1995 (maximum JMA seismic intensity scale 7), the Building Standard Act was revised in order to improve the safety of wooden buildings and to clarify anti-seismic performance level, specifications and building foundation forms. Ground investigations became virtually mandatory. With the enforcement of the Housing Quality Assurance Promotion Act (Housing Quality Assurance Act), the "Housing Performance Labeling System" was established, and it became possible to evaluate and compare the performance of housing based on unified standards. In addition, the construction company was held responsible for defects and rain leaks in the basic structural parts of the house for 10 years. |
Indicators of Anti-seismic Performance Level – “Building Standard Act: Earthquake Resistance Standards“, “Housing Quality Assurance Act: Seismic Grade”
1. “Building Standard Act: Earthquake Resistance Standards“ for protecting human life
The earthquake resistance standards stipulated by Building Standard Act became stricter due to the revision of Building Standard Act on June 1, 1981. So, the standards before June 1, 1981 is called the old earthquake resistance standards, and the same after June 1, 1981 is called the new earthquake resistance standards.
The old earthquake resistance standards:
Level of Earthquake Resistance that buildings do not collapse in an earthquake of JMA seismic scale 5+.
The new earthquake resistance standards:
Level of Earthquake Resistance that buildings are hardly damaged by an earthquake of JMA seismic intensity scale 5+. Level of the same that buildings do not collapse in an earthquake of JMA seismic intensity scale 6+ to 7.
How to check the earthquake resistance standards of buildings
The new earthquake resistance standards apply to buildings that received building certification on or after June 1, 1981. Building certification is a system to certify that a building plan conforms to the building standards stipulated by laws and regulations before the start of construction when constructing a building. In the case of condominiums, construction period takes about 1 year to 1 year and a half from the time of receiving building certification to completion, so condominiums with the completion year of 1981 are considered to have a high possibility of meeting the old earthquake resistance standards.
The time of building certification can be checked at the municipal office, so we recommend that you check with a real estate company for condominiums with the completion year of 1981 to 1983.
2. “Housing Quality Assurance Act: Seismic Grade” for protecting buildings in addition to protecting human life
It is the grade of the "Housing Performance Labeling System" based on the " Housing Quality Assurance Promotion Act (Housing Quality Assurance Act)" enforced in 2000. “Housing Performance Labeling System” is a system in which a third-party organization authorized by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism objectively evaluates the performance of a house based on 10 criteria and allows home buyers to compare the performance of houses according to unified standards.
The Seismic Grade evaluates housing by dividing the quake-resistance performance of a house into three levels of the seismic grade based on two indices of "damage prevention" and "prevention of collapse, etc.". The higher the grade is, the higher the quake-resistance performance is.
What is "Damage Prevention"?
It is defined as a seismic performance level that can withstand an earthquake which may occur once every few decades (JMA seismic scale 5+) to the extent that large-scale restoration is not required.
What is "Prevention of Collapse, etc.”?
It means a seismic performance level to the extent that human life is protected even if damage is received from an earthquake that may occur once every few hundred years (JMA seismic intensity scale 6+ to 7).

Seismic Grade1 is the same performance level as the earthquake resistance standards stipulated by the Building Standard Act. It is a quake-resistance performance that buildings are almost not damaged by an earthquake with JMA seismic intensity scale of 5+, and do not collapse even in an earthquake with the same scale of 6+ to 7. Buildings, however, are damaged by an earthquake with the scale of 6+ or higher to the extent that those need to be rebuilt.
Seismic Grade 2 is the quake-resistance performance level that buildings can withstand an earthquake 1.25 times as much as the same performance level that is assumed by Seismic Grade 1.
In order to be designated as an evacuation place in the event of a disaster, such as a school or hospital, it is necessary to have Seismic Grade of 2 or higher. With Seismic Grade 2, buildings may be damaged by an earthquake with the seismic intensity scale 6+ to 7, but the damages are considered repairable.
With Seismic Grade 2 or higher, the buildings can be certified as “Long-life quality housing”. Long-life quality housing is a house that is designed to live safely and comfortably for a long period of time, and you can receive various tax incentives.
Seismic Grade 3 is the quake-resistance performance level that buildings can withstand an earthquake 1.5 times as much as the same performance level that is assumed by Seismic Grade 1. This grade level is required for fire stations and police stations that serve as the center for reconstruction and first-aid activities in the event of a disaster. With Seismic Grade 3, buildings may be damaged by an earthquake with the seismic intensity scale 6+ to 7, but the damages may be minor and are considered repairable.
How to check the Seismic Grade of a building
"Housing Performance Labeling System" of “Housing Quality Assurance Act " is a voluntary system introduced in 2000, so not all houses obtained an evaluation certificate. In the case of a newly built house, it is possible for you to check with the house builder or the builder office whether or not the housing performance evaluation certificate has been obtained. If it is a custom-built house, we recommend you ask the house builder or the builder office to obtain the evaluation certificate in advance.
In the case of a newly built condominium, it is possible to obtain it by inquiring with the development company. About pre-owned houses and apartments, you can ask the construction company or the management company via real estate agents.
Level of Earthquake Resistance in Japan According to Building Structure
Earthquake Resistant Structure |
This is the most common structure for detached houses in Japan. All buildings built after 1981 must conform to the New Anti-seismic Structure Standard requiring buildings to have an earthquake resistance structure. Seismic resistance structure allows main building structures, namely, posts, walls and floors, to absorb seismic motions. Buildings can be divided into Rigid Structure (constructed rigidly in order to prevent collapse) and Flexible Structure (the main structural parts of which bow flexibly in order to spread the force of seismic motions). |
|---|---|
Damping Structure |
In order to minimize seismic motion, damping walls that absorb seismic energy are constructed within the building. Damping structures can be divided into the Active type, which uses energy such as electricity and the Passive type, which uses physical forces. Compared to earthquake resistant structure, damping structure can reduce seismic intensity by 70-80%. |
Seismic Isolation Structure |
Commonly used for high-rise buildings as part of their foundation, this structure places quake-absorbing devices (isolators) such as laminated rubber that blocks seismic motions from reaching the building. Quake-absorbing devices include laminated rubber, lead, springs, dampers, ball bearings, etc. Furthermore, newly-invented construction methods use a combination of these materials. Seismic isolation structure can reduce seismic intensity down anywhere from ⅓ to ⅕ (less than half) when compared to earthquake resistant structure. |
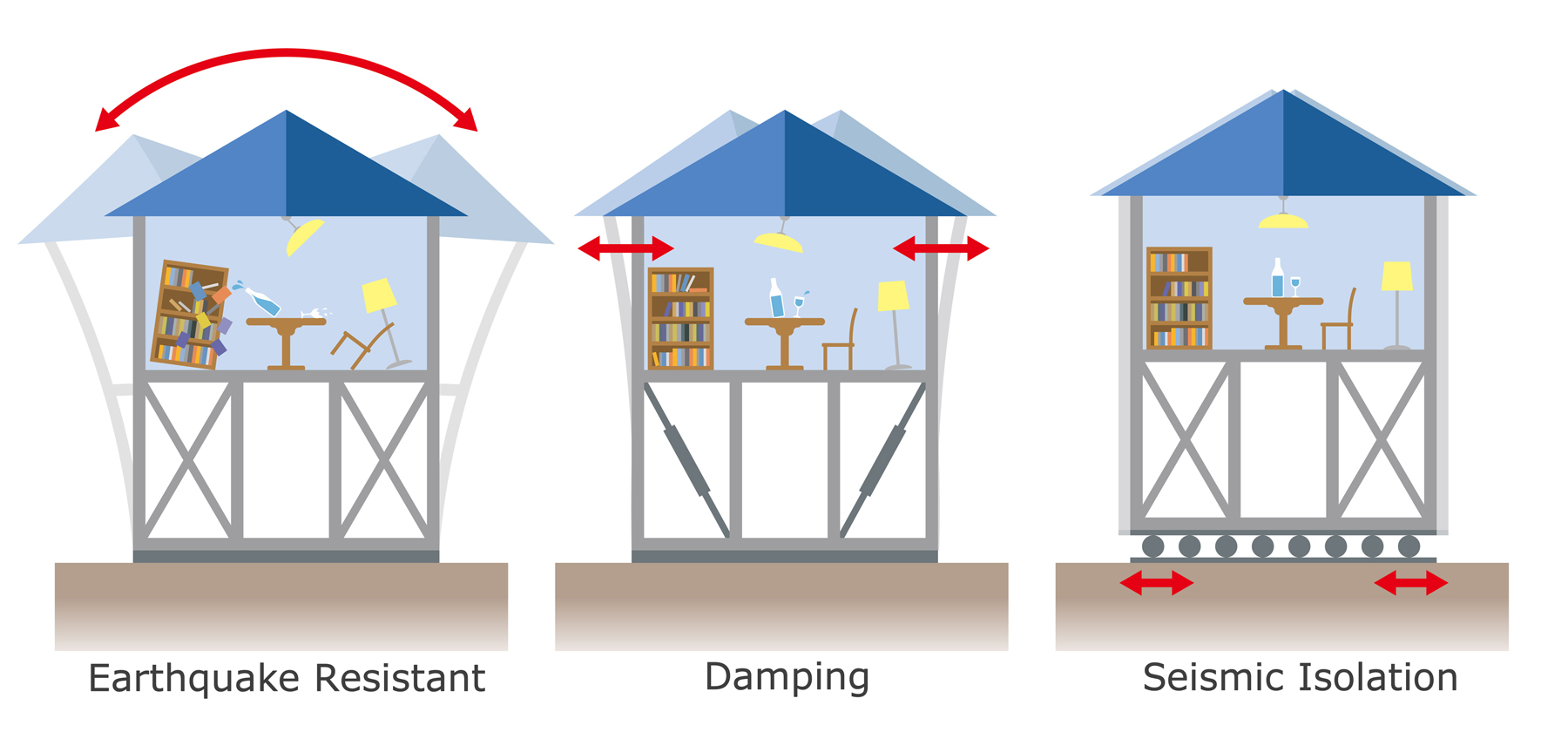
Generally, apartment and office buildings with damping or seismic isolation structures are more secure against earthquakes compared to those with more basic anti-seismic structures.
Types of Building Structures and Materials
Wooden Structure |
Wood is the main material used in these buildings. With that structure, posts and beams serve as the core parts of a given building. Many detached houses in Japan are made of wood. |
|---|---|
Steel Structure (S) |
This refers to buildings primarily using steel materials in their framework. Steel structures are especially suitable for large buildings. |
Reinforced Concrete Structure (RC) |
Building frameworks outfitted with RC (Reinforced Concrete) structure utilize concrete with iron reinforcing bars inside. RC structure takes advantage of both reinforcing bars as well as a steel frame. With Reinforced Concrete structure, steel-made “reinforcing bars” with tolerance against stretching forces, strengthen the “concrete” which resists the compressive forces of the building’s weight. |
Steel Reinforced Concrete Structure (SRC) |
Along with iron frames, buildings with this framework primarily employ concrete with iron reinforcing bars inside. This structure, often referred as “SRC structure,” utilizes both steel and reinforced concrete. Iron poles and beams, which are further supported by iron reinforcing bars, are later filled with concrete. This structure is often applied for high-rise buildings because it provides excellent seismic resistance and is also solid and durable. |
Generally, apartment and office buildings with damping or seismic isolation structures are more secure against earthquakes compared to those with more basic anti-seismic structures.
Risk of Earthquake Damage Depending on Area in Tokyo
(*Reference: Bureau of Urban Development, Tokyo Metropolitan Government)
The disaster risk level also varies depending on the ground, the shape of the land, the density of buildings, etc. In the case of Tokyo, high-risk areas are located on the ground classified as alluvial plains or lowland valleys such as fan-shaped lands, natural levee zones, deltas, and are distributed throughout the old downtown area along Arakawa River and Sumida River, where old wooden and lightweight steel frame buildings are densely gathered. Specifically, the Southern Adachi ward, Arakawa ward, Eastern Taito ward, Western Katsushika ward, Sumida ward and Northern Koto ward areas are considered higher risk due to the reasons described above.
On the other hand, Chiyoda Ward, Minato Ward, Shibuya Ward, etc., where many government offices and foreign companies are located, are considered relatively safe areas in Tokyo.

- Apartments and Houses for Rent in Tokyo
- Listings of popular and luxurious rental apartments, condominiums, and houses designed with expats in mind.

- Apartments and Houses for Sale in Tokyo
- Listings of apartments, condominiums, and houses available for purchase in Tokyo.























